CSAMT surveys utilise EM waves transmitted over a range of frequencies to determine subsurface resistivity. This low-impact, non-intrusive technique has been used extensively by the minerals, geothermal, hydrocarbon, and groundwater exploration industries since 1978, when CSAMT equipment systems first became commercially available. Primary factors affecting resistivities include rock or sediment porosity, pore fluids, and the presence of certain mineral assemblages. For hydrological investigations, CSAMT data may provide critical information about geologic structure, lithology, water table trends, and trends in pore fluid salinity or contamination. Zonge can furnish software for two-dimensional modelling of CSAMT data (SCS2D).
 CONTROLLED SOURCE AUDIO-FREQUENCY MAGNETOTELLURICS (CSAMT) IS A HIGH RESOLUTION RESISTIVITY METHOD COMMONLY USED IN MINERALS EXPLORATION, AND IT ALSO HAS APPLICATIONS IN ENVIRONMENTAL AND ENGINEERING PROBLEMS IN LOW RESISTIVITY ENVIRONMENTS OR WHEN DEEP DATA ARE REQUIRED. LOGISTICALLY, CSAMT HAS MANY ADVANTAGES OVER SOME OF THE OTHER RESISTIVITY METHODS, SINCE IT IS A FAR-FIELD ELECTROMAGNETIC TECHNIQUE. THE FIELD CREW IS USUALLY SMALL (3 OR 4 PEOPLE), THE METHOD WORKS WELL IN NOISY ENVIRONMENTS, AND SURVEY SPEED IS RELATIVELY FAST IF A MULTICHANNEL RECEIVER IS USED. SUCCESSFUL ENVIRONMENTAL PROJECTS INCLUDE GROUNDWATER LOCATION, MAPPING CONTAMINANT PLUMES, MONITORING IN-SITU LEACHING OPERATIONS AT MINES, AND LOCATING BRINE INJECTION LEAKS IN OIL FIELDS.
CONTROLLED SOURCE AUDIO-FREQUENCY MAGNETOTELLURICS (CSAMT) IS A HIGH RESOLUTION RESISTIVITY METHOD COMMONLY USED IN MINERALS EXPLORATION, AND IT ALSO HAS APPLICATIONS IN ENVIRONMENTAL AND ENGINEERING PROBLEMS IN LOW RESISTIVITY ENVIRONMENTS OR WHEN DEEP DATA ARE REQUIRED. LOGISTICALLY, CSAMT HAS MANY ADVANTAGES OVER SOME OF THE OTHER RESISTIVITY METHODS, SINCE IT IS A FAR-FIELD ELECTROMAGNETIC TECHNIQUE. THE FIELD CREW IS USUALLY SMALL (3 OR 4 PEOPLE), THE METHOD WORKS WELL IN NOISY ENVIRONMENTS, AND SURVEY SPEED IS RELATIVELY FAST IF A MULTICHANNEL RECEIVER IS USED. SUCCESSFUL ENVIRONMENTAL PROJECTS INCLUDE GROUNDWATER LOCATION, MAPPING CONTAMINANT PLUMES, MONITORING IN-SITU LEACHING OPERATIONS AT MINES, AND LOCATING BRINE INJECTION LEAKS IN OIL FIELDS.  ROUGH TOPOGRAPHY MAY CAUSE SEVERE DISTORTION IN IMAGING BASED ON AMT DATA ACQUIRED WITH THE ELECTRIC FIELD ORIENTED PERPENDICULAR TO GEOLOGIC STRIKE, I.E. TM-MODE DATA. TOPOGRAPHIC PEAKS CREATE HIGH-ANGLE CONDUCTIVE DISTORTION WHILE TOPOGRAPHIC VALLEYS CREATE HIGH-ANGLE RESISTIVE FEATURES IN TM-MODE AMT DATA. TOPOGRAPHIC DISTORTIONS WILL BE CARRIED THROUGH TO PRODUCE HIGH-ANGLE CONDUCTIVE OR RESISTIVE ARTIFACTS IN INVERSION MODELS UNLESS THE IMAGING PROCEDURE ACCOUNTS FOR THE DISTORTION. SCSINV 1-D RESISTIVITY-DEPTH IMAGES ARE AFFECTED BY 2-D TOPOGRAPHY, WHILE SCS2D 2-D INVERSIONS WITH MODELS INCLUDING A TOPOGRAPHIC PROFILE DO NOT.
TE-MODE MAGNETOTELLURIC DATA, WITH THE ELECTRIC FIELD ORIENTED PARALLEL TO GEOLOGIC STRIKE, IS DISTORTED LESS BY 2-D TOPOGRAPHY THAN IS TM-MODE DATA. HOWEVER COLLECTING TE-MODE IS GENERALLY IMPRACTICAL WHEN COLLECTING CLOSELY SPACED DATA ALONG SURVEY LINES ORIENTED PERPENDICULAR TO GEOLOGIC STRIKE. CONTINUOUS AMT PRODUCTION IS OPTIMIZED WHEN ELECTRIC-FIELD DIPOLES ARE POSITIONED ALONG SURVEY LINES TO COLLECT TM-MODE DATA. IN CONTRAST, ALIGNING ELECTRIC FIELD DIPOLES PERPENDICULAR TO SURVEY LINES TO COLLECT TE-MODE DATA IS TIME CONSUMING (AND EXPENSIVE). AS A RESULT, MOST CLOSELY SAMPLED AMT DATA ARE COLLECTED IN THE SCALAR TM-MODE. CONSEQUENTLY, THIS PAPER FOCUSES MOSTLY ON THE EFFECTS OF TOPOGRAPHY UPON THE INTERPRETATION OF TM-MODE AMT DATA, ALTHOUGH SOME TE-MODE RESULTS ARE INCLUDED.
ROUGH TOPOGRAPHY MAY CAUSE SEVERE DISTORTION IN IMAGING BASED ON AMT DATA ACQUIRED WITH THE ELECTRIC FIELD ORIENTED PERPENDICULAR TO GEOLOGIC STRIKE, I.E. TM-MODE DATA. TOPOGRAPHIC PEAKS CREATE HIGH-ANGLE CONDUCTIVE DISTORTION WHILE TOPOGRAPHIC VALLEYS CREATE HIGH-ANGLE RESISTIVE FEATURES IN TM-MODE AMT DATA. TOPOGRAPHIC DISTORTIONS WILL BE CARRIED THROUGH TO PRODUCE HIGH-ANGLE CONDUCTIVE OR RESISTIVE ARTIFACTS IN INVERSION MODELS UNLESS THE IMAGING PROCEDURE ACCOUNTS FOR THE DISTORTION. SCSINV 1-D RESISTIVITY-DEPTH IMAGES ARE AFFECTED BY 2-D TOPOGRAPHY, WHILE SCS2D 2-D INVERSIONS WITH MODELS INCLUDING A TOPOGRAPHIC PROFILE DO NOT.
TE-MODE MAGNETOTELLURIC DATA, WITH THE ELECTRIC FIELD ORIENTED PARALLEL TO GEOLOGIC STRIKE, IS DISTORTED LESS BY 2-D TOPOGRAPHY THAN IS TM-MODE DATA. HOWEVER COLLECTING TE-MODE IS GENERALLY IMPRACTICAL WHEN COLLECTING CLOSELY SPACED DATA ALONG SURVEY LINES ORIENTED PERPENDICULAR TO GEOLOGIC STRIKE. CONTINUOUS AMT PRODUCTION IS OPTIMIZED WHEN ELECTRIC-FIELD DIPOLES ARE POSITIONED ALONG SURVEY LINES TO COLLECT TM-MODE DATA. IN CONTRAST, ALIGNING ELECTRIC FIELD DIPOLES PERPENDICULAR TO SURVEY LINES TO COLLECT TE-MODE DATA IS TIME CONSUMING (AND EXPENSIVE). AS A RESULT, MOST CLOSELY SAMPLED AMT DATA ARE COLLECTED IN THE SCALAR TM-MODE. CONSEQUENTLY, THIS PAPER FOCUSES MOSTLY ON THE EFFECTS OF TOPOGRAPHY UPON THE INTERPRETATION OF TM-MODE AMT DATA, ALTHOUGH SOME TE-MODE RESULTS ARE INCLUDED.  AT THE SAN MANUEL COPPER MINE IN SOUTHEASTERN ARIZONA, RECOVERY OF COPPER FROM THE OXIDIZED PORTION OF THIS PORPHYRY MINERAL RESOURCE IS BEING ACHIEVED THROUGH A LARGE IN SITU LEACHING OPERATION USING WEAK SULFURIC ACID SOLUTION. IN THE PAST, THIS ACTIVITY WAS COORDINATED WITH OPEN PIT AND UNDERGROUND MINING, BUT IN TODAY'S ECONOMIC CLIMATE, ONLY THE IN SITU OPERATION CONTINUES. THE ACID SOLUTION (20 GRAMS PER LITER) IS INJECTED IN WELLS UN-PRESSURIZED AT VARYING DEPTHS UP TO SEVERAL HUNDRED METERS, USUALLY AT RATES OF ONLY A FEW TENS-OF-GALLONS PER MINUTE. THE COPPER-BEARING PREGNANT LEACH SOLUTION (PLS) IS RECOVERED EITHER IN NEARBY RECOVERY WELLS OR IN COLLECTION AREAS IN THE UNDERGROUND WORKINGS 350 M TO 500 M (1200 TO 1600 FEET) BELOW THE SURFACE. A THOROUGH DESCRIPTION OF IN SITU MINING IN GENERAL AS WELL AS AT SAN MANUEL SPECIFICALLY CAN BE FOUND IN SWAN AND COYNE (1992). DUE TO THE ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF THIS MINING METHOD, THE IN SITU OPERATION AT SAN MANUEL HAS EXPANDED FROM TWO TEST WELLS IN THE MID-1980S TO MORE THAN 900 WELLS COVERING OVER 650,000 SQUARE METERS OF THE OPEN PIT MINE. OVER THE PAST TWELVE YEARS, GEOPHYSICAL SURVEYS HAVE BEEN USEFUL IN BOTH PLANNING AND MONITORING THE EXPANSION OF THE IN SITU FIELD.
AT THE SAN MANUEL COPPER MINE IN SOUTHEASTERN ARIZONA, RECOVERY OF COPPER FROM THE OXIDIZED PORTION OF THIS PORPHYRY MINERAL RESOURCE IS BEING ACHIEVED THROUGH A LARGE IN SITU LEACHING OPERATION USING WEAK SULFURIC ACID SOLUTION. IN THE PAST, THIS ACTIVITY WAS COORDINATED WITH OPEN PIT AND UNDERGROUND MINING, BUT IN TODAY'S ECONOMIC CLIMATE, ONLY THE IN SITU OPERATION CONTINUES. THE ACID SOLUTION (20 GRAMS PER LITER) IS INJECTED IN WELLS UN-PRESSURIZED AT VARYING DEPTHS UP TO SEVERAL HUNDRED METERS, USUALLY AT RATES OF ONLY A FEW TENS-OF-GALLONS PER MINUTE. THE COPPER-BEARING PREGNANT LEACH SOLUTION (PLS) IS RECOVERED EITHER IN NEARBY RECOVERY WELLS OR IN COLLECTION AREAS IN THE UNDERGROUND WORKINGS 350 M TO 500 M (1200 TO 1600 FEET) BELOW THE SURFACE. A THOROUGH DESCRIPTION OF IN SITU MINING IN GENERAL AS WELL AS AT SAN MANUEL SPECIFICALLY CAN BE FOUND IN SWAN AND COYNE (1992). DUE TO THE ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF THIS MINING METHOD, THE IN SITU OPERATION AT SAN MANUEL HAS EXPANDED FROM TWO TEST WELLS IN THE MID-1980S TO MORE THAN 900 WELLS COVERING OVER 650,000 SQUARE METERS OF THE OPEN PIT MINE. OVER THE PAST TWELVE YEARS, GEOPHYSICAL SURVEYS HAVE BEEN USEFUL IN BOTH PLANNING AND MONITORING THE EXPANSION OF THE IN SITU FIELD.  THE SEISMIC REFLECTION METHOD HAS BEEN A HIGHLY SUCCESSFUL TOOL IN OIL AND GAS EXPLORATION FOR HALF A CENTURY, AND IT PRESENTLY ACCOUNTS FOR ABOUT 98% OF ALL GEOPHYSICAL EXPENDITURES WORLD-WIDE. HOWEVER, THE RELATIVELY HIGH COST OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION AND ITS LIMITATIONS IN CERTAIN GEOLOGIC ENVIRONMENTS ARE CONTINUING PROBLEMS. SOME HELP HAS BEEN PROVIDED BY THE MAGNETOTELLURIC (MT) SOUNDING TECHNIQUE, BUT THE COST OF MT IS ALSO QUITE HIGH DUE TO THE LOW NATURAL SIGNAL STRENGTHS BEING MEASURED.
THE CONTROLLED-SOURCE AUDIO-FREQUENCY MAGNETOTELLURICS (CSAMT) TECHNIQUE IS A SHALLOWER-PENETRATING VARIATION OF MT WHICH USES AN ARTIFICIAL SIGNAL SOURCE. THIS PERMITS FASTER AND MORE ECONOMICAL DATA ACQUISITION. CSAMT HAS A PENETRATION OF ABOUT 2 KM IN TYPICAL PETROLIFEROUS ENVIRONMENTS. CSAMT DOES NOT REPLACE SEISMIC BUT FUNCTIONS IN THREE SPECIFIC ROLES: (1) AS A RECONNAISSANCE TOOL TO HELP FOCUS SEISMIC COVERAGE, OR TO HELP AVOID 'NO-RECORD' ZONES; (2) TO ASSIST IN STATIC CORRECTIONS AND IN INTERACTIVE SEISMIC INTERPRETATION; (3) AS A PRIMARY TOOL IN CERTAIN ENVIRONMENTS (VOLCANICS, COMPLEX THRUST AREAS) WHERE SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION IS LIMITED.
AN EXAMPLE OF THE APPLICATION OF CSAMT TO STRUCTURE MAPPING COMES FROM DATA TAKEN OVER TRAP SPRING FIELD, LOCATED IN THE FRONTIER GREAT BASIN OF THE WESTERN UNITED STATES. THE FIELD PRODUCES OIL FROM FRACTURED VOLCANICS AT THE EDGE OF A MAJOR GRABEN FAULT. THE CSAMT DATA DELINEATE THE MAJOR SUBSURFACE FAULTING AND STRATIGRAPHIC RELATIONSHIPS IN THE AREA. THE RESOLUTION OF THE CSAMT SURVEY IS SIGNIFICANTLY BETTER THAN PREVIOUSLY OBTAINED INDUCED POLARIZATION (IP) DATA. DETAILED COMPARISONS WITH ELECTRIC LOG, DRILL HOLE, AND AIR-PHOTO DATA SHOW AN EXCELLENT CORRELATION BETWEEN THE CSAMT FEATURES AND KNOWN GEOLOGY. THE WORK SUGGESTS THAT CSAMT COULD BE USED IN THIS AREA FOR RECONNAISSANCE MAPPING TO DEVELOP SEISMIC PROSPECTS, AT APPROXIMATELY ONE SIXTH THE COST OF SEISMIC.
THE SEISMIC REFLECTION METHOD HAS BEEN A HIGHLY SUCCESSFUL TOOL IN OIL AND GAS EXPLORATION FOR HALF A CENTURY, AND IT PRESENTLY ACCOUNTS FOR ABOUT 98% OF ALL GEOPHYSICAL EXPENDITURES WORLD-WIDE. HOWEVER, THE RELATIVELY HIGH COST OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION AND ITS LIMITATIONS IN CERTAIN GEOLOGIC ENVIRONMENTS ARE CONTINUING PROBLEMS. SOME HELP HAS BEEN PROVIDED BY THE MAGNETOTELLURIC (MT) SOUNDING TECHNIQUE, BUT THE COST OF MT IS ALSO QUITE HIGH DUE TO THE LOW NATURAL SIGNAL STRENGTHS BEING MEASURED.
THE CONTROLLED-SOURCE AUDIO-FREQUENCY MAGNETOTELLURICS (CSAMT) TECHNIQUE IS A SHALLOWER-PENETRATING VARIATION OF MT WHICH USES AN ARTIFICIAL SIGNAL SOURCE. THIS PERMITS FASTER AND MORE ECONOMICAL DATA ACQUISITION. CSAMT HAS A PENETRATION OF ABOUT 2 KM IN TYPICAL PETROLIFEROUS ENVIRONMENTS. CSAMT DOES NOT REPLACE SEISMIC BUT FUNCTIONS IN THREE SPECIFIC ROLES: (1) AS A RECONNAISSANCE TOOL TO HELP FOCUS SEISMIC COVERAGE, OR TO HELP AVOID 'NO-RECORD' ZONES; (2) TO ASSIST IN STATIC CORRECTIONS AND IN INTERACTIVE SEISMIC INTERPRETATION; (3) AS A PRIMARY TOOL IN CERTAIN ENVIRONMENTS (VOLCANICS, COMPLEX THRUST AREAS) WHERE SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION IS LIMITED.
AN EXAMPLE OF THE APPLICATION OF CSAMT TO STRUCTURE MAPPING COMES FROM DATA TAKEN OVER TRAP SPRING FIELD, LOCATED IN THE FRONTIER GREAT BASIN OF THE WESTERN UNITED STATES. THE FIELD PRODUCES OIL FROM FRACTURED VOLCANICS AT THE EDGE OF A MAJOR GRABEN FAULT. THE CSAMT DATA DELINEATE THE MAJOR SUBSURFACE FAULTING AND STRATIGRAPHIC RELATIONSHIPS IN THE AREA. THE RESOLUTION OF THE CSAMT SURVEY IS SIGNIFICANTLY BETTER THAN PREVIOUSLY OBTAINED INDUCED POLARIZATION (IP) DATA. DETAILED COMPARISONS WITH ELECTRIC LOG, DRILL HOLE, AND AIR-PHOTO DATA SHOW AN EXCELLENT CORRELATION BETWEEN THE CSAMT FEATURES AND KNOWN GEOLOGY. THE WORK SUGGESTS THAT CSAMT COULD BE USED IN THIS AREA FOR RECONNAISSANCE MAPPING TO DEVELOP SEISMIC PROSPECTS, AT APPROXIMATELY ONE SIXTH THE COST OF SEISMIC.  THIS PROJECT HIGHLIGHTS TWO IMPORTANT POINTS: 1) THE VERY GOOD AGREEMENT OF RESULTS BETWEEN IP AND CSAMT SURVEY METHODS, AND 2) THE EXCELLENT COMPARISON BETWEEN THE INVERSION MODELS FROM THE TWO SURVEY METHODS. BOTH DATA SETS WERE ACQUIRED BY THE SAME FIELD CREW, USING THE SAME GDP-16 RECEIVER AND GGT-10 TRANSMITTER EQUIPMENT.
THE FOLLOWING EXAMPLE SHOWS THE DIPOLE-DIPOLE DATA AND THE CSAMT DATA THAT WERE ACQUIRED ALONG THE SAME LINE DURING A TRAINING SESSION AT WADI ALMARSAD IN THE KINGDOM OF JORDAN. THE LINE IS ON RELATIVELY FLAT GROUND, CROSSING A NARROW VALLEY. THE ALLUVIAL FILL MATERIAL IS OF AN UNKNOWN DEPTH, BUT EXPECTED TO BE LESS THAN 200 METERS, EXCEPT IN THE CENTER OF THE VALLEY.
THIS PROJECT HIGHLIGHTS TWO IMPORTANT POINTS: 1) THE VERY GOOD AGREEMENT OF RESULTS BETWEEN IP AND CSAMT SURVEY METHODS, AND 2) THE EXCELLENT COMPARISON BETWEEN THE INVERSION MODELS FROM THE TWO SURVEY METHODS. BOTH DATA SETS WERE ACQUIRED BY THE SAME FIELD CREW, USING THE SAME GDP-16 RECEIVER AND GGT-10 TRANSMITTER EQUIPMENT.
THE FOLLOWING EXAMPLE SHOWS THE DIPOLE-DIPOLE DATA AND THE CSAMT DATA THAT WERE ACQUIRED ALONG THE SAME LINE DURING A TRAINING SESSION AT WADI ALMARSAD IN THE KINGDOM OF JORDAN. THE LINE IS ON RELATIVELY FLAT GROUND, CROSSING A NARROW VALLEY. THE ALLUVIAL FILL MATERIAL IS OF AN UNKNOWN DEPTH, BUT EXPECTED TO BE LESS THAN 200 METERS, EXCEPT IN THE CENTER OF THE VALLEY. A CONDUCTIVE CSAMT FEATURE OBSERVED ON THE SUR DE GUERRERO GRID, NEAR THE TOWN OF TAXCO IN GUERRERO, MEXICO, WAS LATER CONFIRMED AS A DISCOVERY BY THIS YEAR'S IMMSA DRILLING CAMPAIGN. THIS FEATURE IS NOW CALLED THE MANTO ESPERANZA VEIJA VEIN. THIS PAPER COMPARES THE GEOLOGY IDENTIFIED BY IMMSA DRILLING WITH THE CSAMT RESULTS MODELED BY ZONGE ENGINEERING.
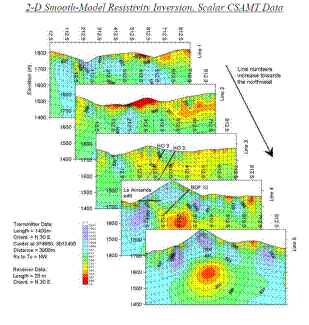
 THE LOS OLIVOS PROJECT IS LOCATED 5 KM EAST OF VALLE DE OLIVOS NEAR HIDALGO DE PARRAL IN THE STATE OF CHIHUAHUA. DURING 1996 CSAMT DATA WERE COLLECTED ALONG 5 LINES FORMING THE OLIVOS GRID. THESE DATA WERE ACQUIRED WITH THE HIGH-POWER (30 KW) ZONGE INTERNATIONAL CSAMT SYSTEM. LA PARRENA, S.A. DE C.V. HAS RELEASED SURFACE GEOLOGY AND DRILL HOLE RESULTS, INCLUDING THE LOS OLIVOS CSAMT DATA. CSAMT IS A HIGH-RESOLUTION RESISTIVITY MAPPING TECHNIQUE THAT USES BROADBAND ELECTROMAGNETIC SIGNALS FOR DEPTH SOUNDINGS.
FOR THIS CSAMT CASE STUDY, THE ZONGE INTERNATIONAL SCS2D INVERSION CODE HAS BEEN USED TO MODEL THESE CSAMT DATA. THE SCS2D INVERSION IS A TWO-DIMENSIONAL (2-D) FINITE ELEMENT SOLUTION THAT NOT ONLY MODELS FLAT-LYING GEOLOGY AND HIGH-ANGLE CONTACTS, BUT ALSO RESISTIVITY CHANGES ASSOCIATED WITH TOPOGRAPHY. THE MODELED RESULTS FOR EACH MODELED LINE IS PRESENTED AS A SMOOTHLY CONTOURED MODELED RESISTIVITY DEPTH SECTION. THE MODELED RESULTS FOR ALL 5 LINES ARE SHOWN AS STACKED DEPTH SECTIONS VIEWED TO THE NORTHWEST, BUT DISPLAYED IN REVERSE ORDER WITH LINES 4 AND 5 SHOWN IN THE FOREFRONT.
THE LOS OLIVOS PROJECT IS LOCATED 5 KM EAST OF VALLE DE OLIVOS NEAR HIDALGO DE PARRAL IN THE STATE OF CHIHUAHUA. DURING 1996 CSAMT DATA WERE COLLECTED ALONG 5 LINES FORMING THE OLIVOS GRID. THESE DATA WERE ACQUIRED WITH THE HIGH-POWER (30 KW) ZONGE INTERNATIONAL CSAMT SYSTEM. LA PARRENA, S.A. DE C.V. HAS RELEASED SURFACE GEOLOGY AND DRILL HOLE RESULTS, INCLUDING THE LOS OLIVOS CSAMT DATA. CSAMT IS A HIGH-RESOLUTION RESISTIVITY MAPPING TECHNIQUE THAT USES BROADBAND ELECTROMAGNETIC SIGNALS FOR DEPTH SOUNDINGS.
FOR THIS CSAMT CASE STUDY, THE ZONGE INTERNATIONAL SCS2D INVERSION CODE HAS BEEN USED TO MODEL THESE CSAMT DATA. THE SCS2D INVERSION IS A TWO-DIMENSIONAL (2-D) FINITE ELEMENT SOLUTION THAT NOT ONLY MODELS FLAT-LYING GEOLOGY AND HIGH-ANGLE CONTACTS, BUT ALSO RESISTIVITY CHANGES ASSOCIATED WITH TOPOGRAPHY. THE MODELED RESULTS FOR EACH MODELED LINE IS PRESENTED AS A SMOOTHLY CONTOURED MODELED RESISTIVITY DEPTH SECTION. THE MODELED RESULTS FOR ALL 5 LINES ARE SHOWN AS STACKED DEPTH SECTIONS VIEWED TO THE NORTHWEST, BUT DISPLAYED IN REVERSE ORDER WITH LINES 4 AND 5 SHOWN IN THE FOREFRONT. 

